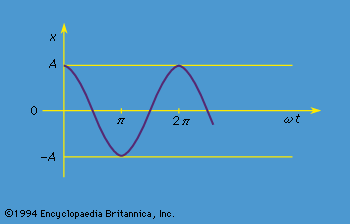
 The function x = A cos t.
The function x = A cos t.| Auf dem Bildschirm werden die momentane Potenzialwerte entsprechend der gewählten Skala vertikal zugeordnet und entsprechend der verfliessenden Zeit, horizontal versetzt projiziert. Die horizontale Schwenkung hängt von der gewählten Zeitskala ab und ist bei jedem links-rechts Lauf des darstellenden Strahles konstant. Hingegend die vertikale Schenkung wird durch die Messung gesteuert. |
 The function x = A cos t.
The function x = A cos t.
|
 |
|
|
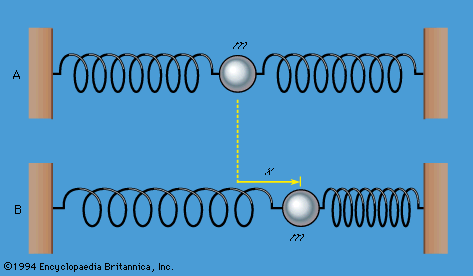 |
| Consider a mass m held in an equilibrium position by springs, as shown in Figure 2A The mass may be perturbed by displacing it to the right or left. If x is the displacement of the mass from equilibrium (Figure 2B), the springs exert a force F proportional to x, such that |
 |
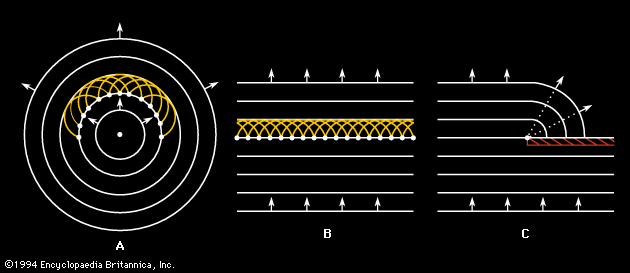
measured in fractions of a second. In addition, during each one-second time interval, a certain number of wavelengths pass a point in space. Known as the frequency of the sound wave, the number of wavelengths passing per second is traditionally measured in hertz or kilohertz and is represented by f.
| Consider a mass m held in an equilibrium position by springs, as shown in Figure 2A The mass may be perturbed by displacing it to the right or left. If x is the displacement of the mass from equilibrium (Figure 2B), the springs exert a force F proportional to x. | ||||
 |
||||
| In was für Medium sich die Radiowellen ausbreiten ist zur Zeit nicht bekannt. Die Schallwellen benutzen die Moleküle zur eigenen Ausbreitung, Wobei jede Molekül des Mediums zur Zentrum einer eigene Schwingung, also Miniwelle wird. Was durchaus auch Parallen bei der Lichtausbreitung hat. Parallele |
||||
 |
||||
 |
||||
| Die Schall - Schwingungen habe durch aus auch einen elektromagnetischen Aspekt. In Festkörper Schwingen die Molekülen in den elektrischen Bindungskräften der Elektronenhülen. Die Gas Moleküle Schwingen in Rahmen der unaufhaltsamen Kollisionen der wärmebedingten Unruhe. Dabei die elektrischnegativen Molekülperipherien, elastisch die Kollisionen in Bewegungsrichtungänderung umsetzen. | ||||
 |
||||
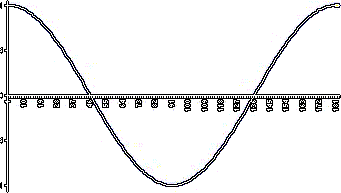 |
||||
|